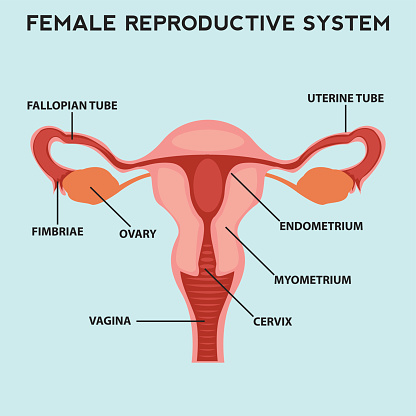
With five convenient locations throughout Cherokee, Cobb, Fulton and North Fulton counties, Atlanta Gynecologic Oncology’s staff and expert surgeons, Dr. Gerald Feuer, Dr. Michelle Glasgow and Dr. Adam Pyrzak provide a full range of services for women with benign and malignant gynecologic conditions.